The Economic Disadvantage to Women: Pink Tax and Gender Wage Gap
On one hand, women are paid less than men for similar work. Women work more and are paid less, according to the International Labour Organisation (ILO). At the same time, they are charged higher than men for similar products. This undeniably puts them at an economic disadvantage. Women already face a social disadvantage owing to gender-based discrimination in society. Many backward sections of society still expect women to leave their jobs after getting married and engage in household work. This social and economic pressure comes together to magnify their predicament.
The ‘Pink Tax’ is not an actual, legally enforced tax. It refers to the difference in pricing of products based on the gender they are marketed and advertised to. Products marketed specifically towards women tend to be priced higher than similar products for men. According to a 2015 study conducted by the New York City Department of Consumer Affairs, products marketed toward women and girls cost an average of 7 percent more than those marketed toward boys and men. This study surveyed 794 products sold in the city.

We can observe such differences in pricing in our daily lives. Disposable razors for women, which are often pink, are priced around Rs.55, whereas a black/blue razor for men would cost around Rs.20. Despite them having more or less the same ingredients, the same brand and the same quantity, perfumes for women may cost more than for men.
Women’s shampoo costs up to 48% more than men’s shampoo which is the same except for the scent. This is not only applicable to adult products. It can also be seen in children’s toys and school uniforms. Girls’ toys cost more than comparable boys’ toys. For example, a helmet for boys will cost less than one that is pink in color.
There is a further effect on women’s mental health when a specific standard of beauty is promoted while marketing these products.
Tariff on different goods is also a factor that affects this gender-based pricing. Tariffs refer to the tax paid by retailers for importing goods. For example, in the United States, the female versions of certain products like wool jackets, leather boots and cotton shirts, face higher tariffs than male versions. Certain male clothing products, like bathing suits and wool suits, are also subject to higher tariffs. However, overall, tariffs on women’s clothing are higher.
However, high tariffs do not completely justify this phenomenon as the pink tax can be seen in domestic products as well as services.

Many countries, including the United States, also continue to impose taxes on menstrual sanitary products. For women of lower income groups, this restricts their access to essential hygiene and sanitation. They are forced to use old rags and clothes, which increases their risk for multiple health complications like HPV and incontinence.
After persistent campaigning by activists,12 per cent GST on menstrual sanitary products was removed by the central government in 2018.

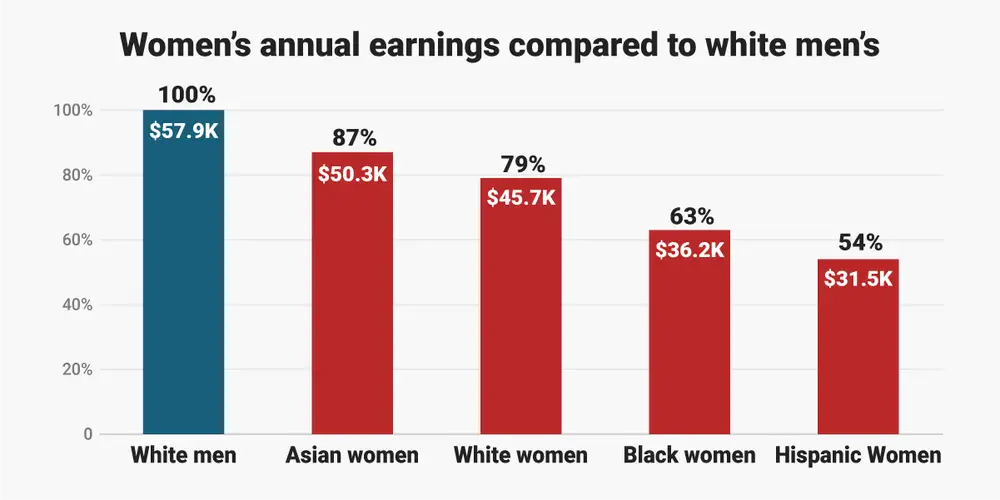
The International Labour Organisation (ILO) points out that women often get paid less for the same work as men. On average, there is a 19 per cent gap between women’s salaries and men’s salaries across all sectors in India, and more so in agriculture, where women undertake 80 per cent of the work. Internationally, women of color are at a greater disadvantage. Black women earn 64 cents to a white man’s dollar and Hispanic women only earn 56 cents. Even in income during retirement, women only receive 70 per cent of what men do.
The gender divide is also distinctly visible in the proportion of women in leadership roles in workplaces. Male dominance is widespread across management positions in several sectors and industries. According to a survey conducted in 2021, women held only 10% of management roles and were only 5% of CEOs in India.
The status and rights of women in society are developing, slowly and steadily. However, gender-based inequalities like Pink Tax and Tampon Tax pose as obstacles in the struggle for creating an equal world for men, women and other genders. Such financial burdens must be eliminated where they are not justified. As a society, we must try our best to minimize discrimination among sections and provide them with equal opportunities.
By Mihika Singh
Also Read:
PLAYING THE MARKET: STOCKS OR SLOTS-Deciphering the fine line
Playing the market: Stocks or Slots?Deciphering the Fine line The world of finance, the stock …
Social Echoes: Amplifying Sales through Digital Word-of-Mouth
Social Echoes: Amplifying Sales through Digital Word-of-Mouth It is a truth universally acknowledged that E-Commerce …
Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Analysis of the IMEEEC
Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Analysis of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEEC) Abstract The …
