The Upsurge Of Subscription Economy
In recent times, subscription model has spread like a wildfire in the business world across different industries. Every industry ranging from automobile to pharmaceutical, entertainment to financial services have successfully developed their own subscription models generating revenue. It has become one of the most prominent business models for service providing businesses like OTT platforms, modern softwares, etc. The subscription economy has grown by more than 435% in the past 9 years. Predominantly, every other industry has seen at least one successful subscription model.
What is a subscription business model?
A subscription business model is a business model where a customer pays a fixed amount at regular intervals in a recurring nature to access a product or a service. Rather than selling a product or service in a single transaction, payments at regular intervals like annually or monthly are charged by the vendor from the customer. In this way even a very expensive product or service can be accessed easily by the customers as and when they require it by paying a relatively lower subscription fee. These models can also be used by vendors to convert one time sale of goods into a recurring sale and can help in building brand loyalty.
The Rise of Global Subscription Economy
The concept of subscription was first introduced by newspaper and book publishers of Europe in the late 1600s. The people in the UK were able to subscribe to the services of a milkman, magazine subscriptions. By the time of 20th century subscription packages were available in a variety of businesses like operas, cinemas, literature, etc. With the rise of technology and Software as a Service (SaaS) products, many companies moved from revenue model of one-time sale to subscription models.
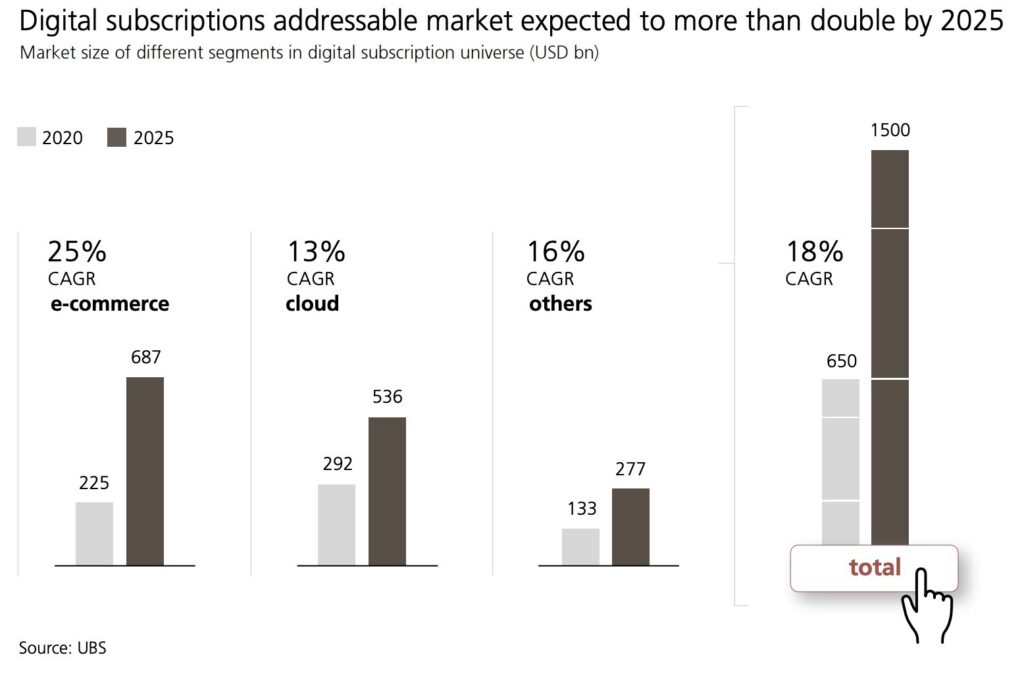
In the present economy, subscription model runs a range of industries and verticals like Netflix in media, Amazon Prime in e-commerce, Adobe in SaaS, etc. The subscription economy stands at $65o billion as of 2020 and is expected to grow with a CAGR of 18% to $1.5 trillion by year 2025. The E-commerce accounted for $225 billion and cloud services stood at $292 billion forming a major part of the subscription economy.
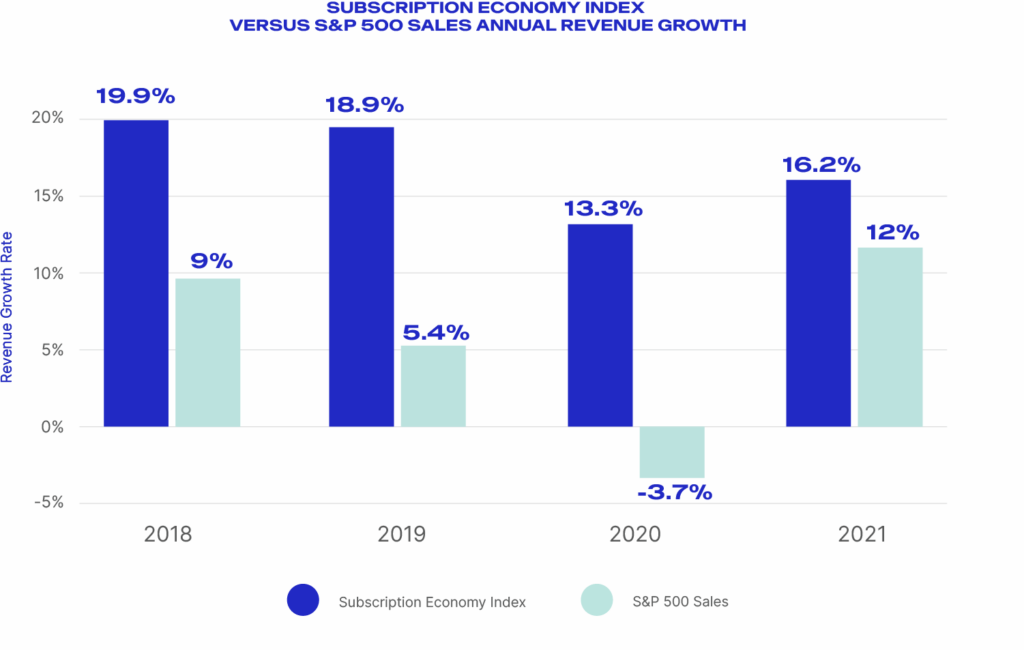
The Subscription Economy Index has experienced a 17.5% 10-year CAGR in annual revenue growth versus a 3.8% for the S&P 500, and the distance between those two figures is increasing.
The Curious Case of Adobe
Adobe, which is regarded as one of America’s most important technology companies and is used by 90% of the world’s creative professionals, took a risk in 2013 by introducing a significant change in its revenue model. Adobe used to sell software in physical boxes as a one-time purchase option for individuals for $1299. Such high prices created an entry barrier for customers because any casual or inexperienced creator could not afford to invest such a large sum. This left them with no choice but to use pirated versions of the software, resulting in a significant loss of revenue for the company. As a result, Adobe launched its Creative Cloud Software as a Service (SaaS) model in 2013. It gave users the option of subscribing to the services by paying a regular monthly fee of $70. As a result, many small creators who were previously unable to purchase entire software due to budget constraints were now able to afford the company’s services. This also provided the company with a recurring revenue stream. This critical move proved successful, as the company’s revenue increased from $4.3 billion in 2013 to $17.6 billion in 2022. Subscription services now account for nearly 90% of revenue.
The Pioneer of OTT Industry
Starting as a brick and mortar DVD seller, Netflix traversed a long path to become the most dominating company in the OTT segment. Netflix started off back in 1997 as a subscription-based DVD mailing service provider which used to provide DVDs for a stipulated subscription period. Along with advancements in technology the company transformed its revenue model to Subscription Video on Demand model (SVoD) where the consumer subscribes for a vast library of content from a variety of plans with varied time periods like monthly, quarterly or annually. The company had a monthly Average Revenue per User (ARPU) of $11.6 worldwide which generated a revenue of $29.6 billion for the company.
The Risky Move of the Management
GoPro, the world’s biggest action camera company, ventured into Direct-to-Consumer subscription model which transformed the company into a higher margin and more profitable business. The subscription comes with a range of benefits ranging from cloud storage, camera replacements, premium access, etc. Once considered a crazy gamble of the management, the move proved to be tremendously successful. The company successfully managed to garner over 2 million subscribers which translates into a revenue of over $100 million to the company.
How customers get attracted to subscriptions?
There are many factors which attract consumers towards subscribing for a product or service.
- Convenience is a prominent factor which induces customers to take up a subscription. By subscribing to a product, a customer is relaxed from reordering again and again. The subscribed product or service is delivered automatically periodically making it convenient for the customers.
- Pricing is one other factor which plays a major role in attracting customers. A customer is more comfortable in subscribing for a product such as a software rather than purchasing the whole in one shot. Also, since the pricing is set at a lower level, more and more customers get attracted which results in increased potential customer base of a business.
- From a psychological point of view, a customer makes decisions using two systems, one is intuitive and reflexive and the other is regulated and conscious. A simple moment of thought before adding a item to cart can add up overtime. Therefore, subscription helps a customer to reduce cognitive time while shopping.
Types of Subscription Models
- Replenishment Model – In this model customer subscribes for a product or service and receives regular delivery of same type of product like groceries, food, medicines, etc. The are also known as subscribe and save model. Example- Amazon’s subscribe and save.
- Access Subscription Model – This is the most popular subscription model where people a monthly or yearly fees to access specific service or content. This subscription model is most commonly used by SaaS providers. Example – Netflix, Adobe Photoshop, Skillshare, etc.
- Curation Subscription Model – In this model subscribers regularly purchase curated boxes of products like clothing, pet supplies, beauty products, etc. Example- FabFitFun, BarkBox, HelloFresh, etc.
- Freemium Model – In freemium model, the company offers the base version of their product or service for free with an expectation that a certain number of users will convert into paid subscribers to avail the premium services. The customer acquisition cost of this model is comparatively very low. Example- Spotify, YouTube, etc.
Benefits of Subscription Models
- One of the biggest advantages of subscription model is that it creates a reliable source of recurring revenue.
- They help in creating a strong customer base and increases customer loyalty. The business can focus more on existing subscribers and spend less time on acquiring new customers.
- In the long term, subscription businesses have better customer retention than businesses that rely on one-time purchases.
- By making their offerings flexible, subscription business helps to reduce the churn rate of the customers. Average churn rate for subscription services is estimated to be around 6-8%.
- Subscription models help business to lower customer acquisition cost (CAC) by nurturing good customer relationships.
- Another advantage is that it leads to better cash flows and business is able to effectively maintain required inventory levels.
Industries upcoming with subscription models
- Automobile Industry – Nowadays people have the option to subscribe to car rental services which allows them to select from a variety of options available before them. It gives the customer a feeling of ownership without any cost and responsibility. According to surveys almost 46% customers said that they would opt for vehicle subscriptions. Audi, Nissan and Porsche are among the few to offer subscription services to their customers.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) – It is a method of purchasing online softwares like Adobe in exchange of a periodic payment. The global SaaS industry is valued at $216 billion in 2021. Some of the examples are Cisco Webex and Dropbox.
- Entertainment – Entertainment includes a variety of options ranging from movies to songs and documentaries. Large corporations are like Netflix and Spotify are operating successfully using the subscription model where customers can choose from the unlimited content present on these platforms.
- Educational and Professional Development – With such a fast moving world, people need to keep their skillset updated and increase their pace of learning. Platforms like LinkedIn Learning provide with a range of development courses to their subscribers helping them to remain relevant in the industry.
- Gaming – The gaming industry is on a boom and the recent trend is the rise of subscription based gaming providing access to a variety of options rather than a single game. Subscriptions like Xbox Game Pass and PlayStation Now are becoming famous among the gaming community.
Major drawbacks of the subscription models
- There is always a risk of high cancellation rates is the business fails to upgrade its offerings to the customers.
- Contract aversive behavior of customer is another significant drawback in the subscription business as the customer naturally doesn’t want to get bound by a future contract.
- Initial signing up avoidance on part of customer also creates a major challenge for the company to persuade the customer to opt for the service.
- Constant need to provide new value makes it difficult for the companies to maintain the churn rate below the limits.
By Mudit Lakhotia
Also Read:
PLAYING THE MARKET: STOCKS OR SLOTS-Deciphering the fine line
Playing the market: Stocks or Slots?Deciphering the Fine line The world of finance, the stock …
Social Echoes: Amplifying Sales through Digital Word-of-Mouth
Social Echoes: Amplifying Sales through Digital Word-of-Mouth It is a truth universally acknowledged that E-Commerce …
Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Analysis of the IMEEEC
Unlocking the Potential: A Comprehensive Analysis of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEEEC) Abstract The …
